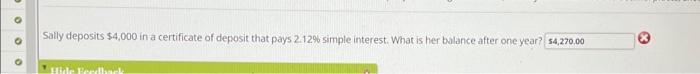
Sally deposits 4000 in a certificate – Sally’s recent deposit of $4,000 in a certificate of deposit (CD) exemplifies a wise financial decision, highlighting the benefits and considerations associated with this investment vehicle. CDs offer a secure and stable way to grow savings, providing guaranteed returns over a specified term.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of Sally’s CD deposit, exploring the reasons behind her investment, its financial implications, and the broader landscape of CD investment strategies. By understanding the mechanics and nuances of CDs, individuals can make informed decisions about their own financial goals.
Certificate of Deposit Overview

A certificate of deposit (CD) is a savings account with a fixed term and interest rate. When you open a CD, you agree to deposit a certain amount of money for a specific period, typically ranging from a few months to several years.
During that time, you cannot withdraw the money without paying a penalty. In exchange for your commitment, you earn a higher interest rate than you would on a regular savings account.
Features and Benefits of CDs, Sally deposits 4000 in a certificate
CDs offer several features and benefits, including:
- Fixed interest rates:CDs offer fixed interest rates, which means that you know exactly how much interest you will earn over the life of the CD. This can be a valuable feature, especially in a rising interest rate environment.
- Higher interest rates than regular savings accounts:CDs typically offer higher interest rates than regular savings accounts. This is because banks are willing to pay more interest for money that they can count on having for a longer period.
- FDIC insurance:CDs are insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) up to $250,000 per depositor, per insured bank. This means that your money is safe even if the bank fails.
Types of CDs
There are several different types of CDs, including:
- Traditional CDs:Traditional CDs are the most common type of CD. They offer a fixed interest rate for a fixed term. You can choose from a variety of terms, ranging from a few months to several years.
- Jumbo CDs:Jumbo CDs are CDs with a large deposit amount, typically $100,000 or more. They offer higher interest rates than traditional CDs, but they also have higher minimum deposit requirements.
- Bump-up CDs:Bump-up CDs allow you to increase the interest rate on your CD one time during the term. This can be a valuable feature if interest rates rise during the life of your CD.
- Callable CDs:Callable CDs give the bank the option to call back the CD and repay you early. This can be a disadvantage if interest rates fall during the life of your CD.
Sally’s CD Deposit

Sally’s decision to deposit $4,000 in a certificate of deposit (CD) is a significant financial move. This deposit can potentially have several implications for her financial situation, both in the short and long term.
Reasons for Sally’s Deposit
There are several potential reasons why Sally may have chosen to make this deposit. She may be saving for a specific financial goal, such as a down payment on a house or a new car. Alternatively, she may be seeking a safe and stable place to store her money while earning a modest return.
Financial Implications of Sally’s Deposit
The financial implications of Sally’s deposit will depend on the terms of the CD, including the interest rate and the maturity date. If the interest rate is high, Sally could earn a substantial amount of interest over the life of the CD.
However, if the interest rate is low, her earnings will be more modest.
The maturity date of the CD will also affect the financial implications of Sally’s deposit. If the maturity date is short, Sally will have access to her money sooner. However, if the maturity date is long, she will have to wait longer to access her money.
In some cases, there may be penalties for withdrawing money from a CD before the maturity date.
CD Investment Strategies
Certificate of Deposits (CDs) offer various investment strategies tailored to specific financial goals. Understanding these strategies is crucial for optimizing returns and minimizing risks.
There are three primary CD investment strategies:
Fixed-Rate CDs
Fixed-rate CDs offer a fixed interest rate for the entire term of the investment. They provide stability and predictability, making them suitable for risk-averse investors seeking steady returns.
Advantages:
- Guaranteed return at a fixed rate
- Low risk
- Easy to understand and manage
Disadvantages:
- Lower returns compared to other investments
- Penalty for early withdrawal
Variable-Rate CDs
Variable-rate CDs offer an interest rate that fluctuates with market conditions. They provide potential for higher returns, but also carry more risk.
Advantages:
- Potential for higher returns
- Flexibility to adjust to changing interest rates
Disadvantages:
- Unpredictable returns
- Risk of lower returns during periods of falling interest rates
Bump-Up CDs
Bump-up CDs offer a combination of fixed and variable rates. They start with a fixed rate that can be “bumped up” to a higher rate if market interest rates rise.
Advantages:
- Potential for higher returns than fixed-rate CDs
- Protection against falling interest rates
Disadvantages:
- Lower returns than variable-rate CDs if interest rates rise significantly
- May have a cap on the maximum interest rate
Choosing the best CD investment strategy depends on individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. Fixed-rate CDs are suitable for investors seeking stability and predictability, while variable-rate and bump-up CDs offer potential for higher returns with increased risk.
CD Interest Rates and Returns: Sally Deposits 4000 In A Certificate
The interest rate offered on a CD is determined by a combination of factors, including the prevailing market interest rates, the financial health of the issuing bank, and the term of the CD. Market interest rates are set by the Federal Reserve and fluctuate based on economic conditions.
Banks typically offer CD rates that are slightly below the prevailing market rate, as they need to cover their own operating costs. The financial health of the issuing bank can also affect CD rates. Banks with a strong financial track record are more likely to offer competitive CD rates, as they are perceived as being less risky.
Finally, the term of the CD also affects the interest rate. Longer-term CDs typically offer higher interest rates than shorter-term CDs, as the bank is locking in your money for a longer period of time.
Historical CD Interest Rates
The following table shows historical CD interest rates for various terms:
| Term | 1990 | 2000 | 2010 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-year | 8.12% | 5.13% | 0.90% | 0.10% |
| 3-year | 8.25% | 5.28% | 1.05% | 0.20% |
| 5-year | 8.40% | 5.43% | 1.20% | 0.30% |
Factors that Can Affect CD Returns
In addition to the interest rate, there are a number of other factors that can affect CD returns. These include:
- Inflation:Inflation can erode the value of your CD returns over time. If the inflation rate is higher than the interest rate on your CD, you will lose purchasing power over time.
- Taxes:CD interest is subject to federal and state income taxes. This can reduce your overall return.
- Fees:Some banks charge fees for CDs, such as early withdrawal fees. These fees can reduce your overall return.
CD Risks and Considerations
Investing in certificates of deposit (CDs) generally carries low risk compared to other investment options. However, there are certain risks to consider before investing in CDs.
Interest Rate Risk
Interest rates can fluctuate over time, and changes in interest rates can affect the value of your CD investment. If interest rates rise, the value of your CD may decrease. This is because investors may be able to find higher-yielding CDs or other investment options, which could make your CD less attractive.
Inflation Risk
Inflation is the rate at which prices for goods and services increase over time. If inflation rises, the purchasing power of your CD investment may decrease. This is because the interest you earn on your CD may not keep pace with inflation, which could erode the value of your investment over time.
Liquidity Risk
CDs are typically less liquid than other investment options, such as savings accounts or money market accounts. This means that you may not be able to access your funds immediately if you need them. If you withdraw your funds from a CD before the maturity date, you may have to pay a penalty.
Credit Risk
Credit risk is the risk that the issuer of your CD may default on its obligation to pay interest and principal. This is a rare occurrence, but it is important to consider before investing in a CD. You should only invest in CDs issued by banks or credit unions that are well-rated and have a strong financial track record.
Mitigating CD Risks
There are several ways to mitigate the risks associated with investing in CDs. One way is to diversify your investments. This means investing in a variety of different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate. By diversifying your investments, you can reduce the risk that you will lose all of your money if one investment performs poorly.
Another way to mitigate CD risks is to choose CDs with shorter maturities. This will reduce your exposure to interest rate risk and inflation risk. However, you may earn a lower interest rate on shorter-term CDs.
Finally, you can consider investing in CDs that are issued by banks or credit unions that are well-rated and have a strong financial track record. This will reduce your exposure to credit risk.
Considering Other Investment Options
Before investing in CDs, it is important to consider other investment options that may be more appropriate for your individual needs and risk tolerance. Some other investment options to consider include:
- Savings accounts
- Money market accounts
- Bonds
- Stocks
- Real estate
Each of these investment options has its own risks and rewards. It is important to do your research and understand the risks involved before investing in any investment option.
Question Bank
What is the significance of Sally’s $4,000 deposit in a CD?
Sally’s deposit demonstrates her understanding of financial planning and her commitment to saving and growing her wealth. CDs offer a safe and reliable way to earn interest on her savings, helping her achieve her long-term financial goals.
What are the potential reasons for Sally’s CD deposit?
Sally may have deposited the money to save for a future purchase, such as a down payment on a house or a new car. Alternatively, she may be seeking a low-risk investment option to generate passive income or supplement her retirement savings.
What are the financial implications of Sally’s deposit?
Sally’s deposit will earn interest at a fixed rate over the term of the CD. The interest earned will be added to her account balance, increasing her overall savings. However, she will not have access to the funds until the CD matures, which could impact her liquidity.